The 7010 has been verified to work (you can use that ME region as well) and your CPU is vPro (AMT) capable so it’s certainly something BIOS-config related. Make sure you have the latest Dell BIOS applied (I verified that it does include a MEBx module inside). Then reset BIOS default settings and look for any option to enable MEBx or similar. You can make it work. Oh and thank you very much for your donation aquarc. 
I understand it should work, but it doesn’t. I looked in the entire BIOS options and there is no option for ME/MEBx (on my older Optiplex machines, there was a separate main entry for ME). I recall updating the BIOS on this Optiplex a month ago when I posted first. I see that the latest bios for the 7010 is from 2015 so I already have the latest one. I didn’t reset to default BIOS settings, I can try that tomorrow - though that shouldn’t make a difference (should it?).
Is it at all possible you uploaded a different file or that you generated it form a different file than the one in my link? What else could it be?
The ME region was fixed from your own dump and I have verified that the settings to enable AMT are set. The latest BIOS for 7010 is A25 from May 2017 as can be seen here. It is always recommended to reset BIOS settings to default after an update and then re-adjust accordingly, that’s why I said that. Can you show a report from MEInfo tool with -verbose parameter?
I was just coming to post that I found the latest bios to be A25 from May 2017 and that I’m no longer sure I have the latest BIOS. I’ll try everything you suggested tomorrow as I’m now away from it. What’s the actual step by step here:
- set jumper to service mode
- flash bios to A25
- flash your fixed ME fw again
- reboot
- set jumper back to normal mode
- reset bios to defaults
- see if ME appears in BIOS
Is that the right sequence?
- Flash BIOS to A25
2. Reboot
3. Reset BIOS to defaults
4. Reboot
5. Adjust BIOS settings to your liking
6. Shutdown
7. Set jumper to Service mode
8. Flash me_fix.bin via "fpt -rewrite -me -f me_fix.bin"
9. Shutdown
10. Set jumper back to normal mode
11. Perform ME reset via "fpt -greset"
12. Reboot
13. AMT should be operational
I did all those steps very carefully in the order indicated. There is no ME or MEBx in the BIOS, but there is one when pressing F12 (boot menu). There I can see MEBx and was very happy, but entering it I can see the 4 entries:
- MEBx Login
- Intel ME General Settings
- Intel AMT configuration
- MEBx exit
I can only select the 1st and last option, and for the first option it asks me for a password, which I don’t know. I googled and tried “admin” as password but it didn’t work. CTRL+P after reboot still doesn’t do anything.
What am I missing? I’m not sure if this MEBx screen was accessible before (I never pressed F12 until now) and whether it was again only allowing “Login” or “Exit” to be chosen.
Alright, the fix worked, you now have access to MEBx and AMT is enabled but not yet provisioned. It is not necessary to access MEBx via Ctrl+P, the OEM can change that. In Dell’s case, I assume they added it via the F12 menu or similar. At MEBx, it is normal to see only the 1st and 4th option when AMT is unprovisioned. You’re supposed to login with default password (admin) and then provision it. Although it shouldn’t be required in your case, to reset the password to default you have to shutdown, remove all power (AC/DC, battery) and perform a RTC reset.
Like I said, “admin” didn’t work. How exactly do you do an RTC reset on this model? I didn’t see a coin battery on the motherboard - at least where I could look (I didn’t dismantle everything like PSU, etc)
Strike that - it was a silly oversight on my part: my keyboard has the numpad integrated on the main keys, and num lock was on, so tapping “i” was actually typing “5”, so “admin” became “adm5n” and gave an error. It worked afterwards and asked me to change it (spent 5 minutes and had to google to see that i need a super strong password).
I was able to configure it and access the web page on port 16992.
New problem: VNC access (KVM) is not working … should it work? While configuring AMT in the MEBx bios, there was a “KVM Feature Selection” option which is set on “Enabled”, so I thought KVM via VNC should work like on my other Lenovo small server, on port 5900 (this guy can do it on the Optiplex 7010). Any clues?
Port 5900 is not open. Is it possible that your fixed ME firmware doesn’t have KVM via VNC? If yes, would you be able to include it?
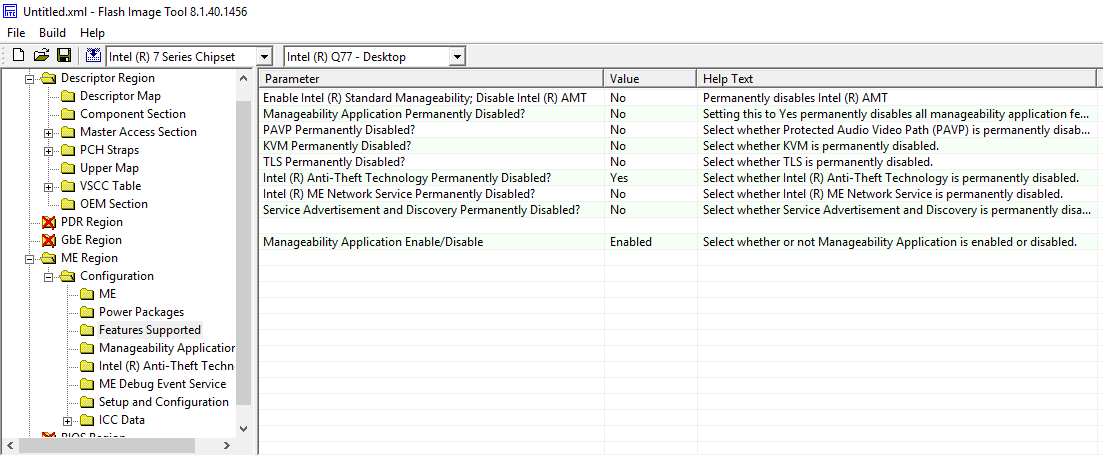
I’ve never had and/or configured an AMT system so I’m not able to help on its features. But as you can see, everything that should be enabled to make AMT work is enabled (you can verify yourself via Flash Image Tool):
Try to use MeshCommander to config and test the AMT.
http://www.meshcommander.com/meshcommander
Well, port 5900 is not open (nothing is listening on it) so no external tool can help. It seems KVM via VNC is just not available or not actually working in this ME firmware (though it is definitely possible in other Optiplex 7010 like seen here). I may be out of luck ![]()
The firmware is capable, the problem is not there. Read the MEBx User Guide, it should guide you on how to properly set KVM.
I did everything in there. Also, there are literally only two KVM related options in the settings (one for Enable KVM feature selection, and one for KVM user consent) so it’s not like there is a complicated configuration to do. Nothing is listening on the 5900 port. If you have other ideas then by all means. The blogger guy I linked above did the same and it works in his case.
I have another Lenovo small server with MEBx that looks the same, and KVM works (VNC is listening on port 5900).
Either it’s disabled, or it fails to start (are there any logs anywhere? the bios logs don’t show anything), or the ME firmware you fixed doesn’t actually enable it (I know you think it should be there though).
As I told you with MCommander you will be able to activate/deactivate KVM and user consent and check the settings.
Have a look.
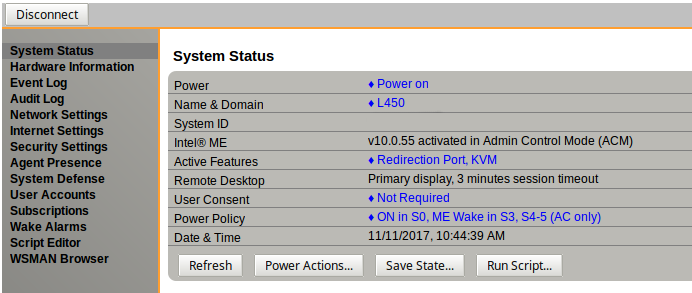
I’ll try next time I have access to a Windows machine (I see MCommander is windows only) and will let you know - though the above screenshot looks the same as the options I already activated in the MEBx bios, where I already enabled the KVM feature.
As explained at the MEBx User Guide, the MEBx option is not enough. You need to have the Corporate/5MB drivers installed and download the AMT SDK to run a configuration program and so on. MeshCommander is an alternative to the latter from what I’ve understood but I would trust those (like fs-esprimo) who have actually activated AMT and know how it works.
If you are on Linux you can try to install MeshCentral 2 as a server on a computer without AMT.
Then you can manage and set all AMT computers accessing that server from any computer with or without AMT.
I am using that on Linux and it is working great, print screen it is taken from a Linux comp that access MeshCentral 2
http://www.meshcommander.com/meshcentral2
I will give all this a go and will be able to confirm after i actually try it. I’m away for a short while right now, but I’m a bit stumped by what you guys are suggesting: Are you saying that even though the KVM is enabled in MEBx and even though the IP is not listening on port 5900 (but is listening on port 16992 and shows the AMT options), there is some sort of a hidden way to still enable KVM which would then accept VNC connections on port 5900, which requires installing 3rd party tools just to enable KVM on port 5900?
I am on Linux and can access a few machine son that network remotely. Can MeshCentral do the same things as MeshCommander (enable KVM, etc)?
Is it possible that my unit simply does not have KVM?
KVM it is present from AMT 6 up to latest.
If I remember correct you need to enable also legacy redirection ports to be able to connect on 5900 and for that you need MeshCommander or MDTK.
Or the hard way is to read the documentation for AMT SDK and make your own program that send commands to AMT.
MeshCentral 2 it is a server solution to manage computers and yes accessing MC2 server via browser you can do almost all like MeshCommander.