@ all users with an Intel AHCI or RAID system
Preliminary note:
Since Intel is offering a big variety of different Intel AHCI and RAID driver versions, which belong to different development branches (MSM, RST, RSTe), it is not easy for the users to find the "best suitable" one out of them.
This thread may help you to "find the needle in the haysack".
Which are the "best" Intel AHCI/RAID drivers?
Since there is no Intel AHCI/RAID driver available, which is suitable or may be even perfect for all different Intel SATA Controllers, Operating Systems and driver installation/integration procedures, I am offering a variety of Intel AHCI/RAID drivers, which belong to different development branches (MSM, RST and RSTe).
To make the selection of the appropriate driver for your special system easier for you, I have tried to list the advantages/disadvantages of the different Intel AHCI/RAID drivers development branches:
-
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager (MSM) drivers
(first Intel AHCI/RAID driver series, outdated since several years)- Advantages:
- best chances for a successful integration into Windows XP, if the user doesn’t know the exact Intel SATA AHCI/RAID Controller specification of his system
- no problems by using any Virtualisation Software instead of doing a clean install of the OS
- Disadvantages:
- suboptimal performance, especially with actual hardware components
- no TRIM support (only relevant for SSD users)
- outdated driver model line, no support of the newest Intel Chipsets
- Advantages:
-
"conventional" Intel(R) Rapid Storage Technology (RST) drivers
(using just 1 driver named iaStor.sys)- Advantages:
- very good WRITE performance, especially on RAID0 systems with enabled Write-Back Caching
- TRIM support (only relevant for SSD users)
- evoke a very stable storage function and usage
- Disadvantages:
- further development has been stopped by Intel
- some features of the newest Intel chipsets are not supported, may not even work with 8- and 9-Series Chipsets
- increased chance of a driver integration failure (more sensitive to any mistake/unsure handling than the MSM drivers)
- Advantages:
-
actual Intel(R) Rapid Storage Technology (enhanced RST) drivers
(using an additional SCSI Filter driver, should better be named RST(e) drivers)- Advantages:
- do support all new features of the actual Intel chipsets
- TRIM support (only relevant for SSD users)
- continuous further development by Intel
- Disadvantages:
- limited support of older chipsets
- RAID0 usage with older chipsets: much less performant than the latest RST drivers
- Advantages:
General personal statements:
- The newest drivers are not always the best. Even if they should be the best for some systems, this is not automaticly valid for all hardware configurations.
- Users with an older Intel chipset should always keep in mind, that the chipset manufacturer Intel only develops drivers for the newest and for the upcoming chipsets and not for the older ones. Although many of the new drivers are backwards compatible with older AHCI and RAID Controllers, they are not or may not be optimized for them. A successful installation of a new Intel RAID driver onto an old Intel platform RAID system does not automaticly mean, that it will flawlessly work.
-
The choice of the "best" (=fastest) Intel AHCI/RAID driver is more difficult for RAID than for AHCI users.
According to my experience there are no big differences regarding the performance of the various Intel AHCI/RAID driver versions, if they are used in AHCI mode, wheras the differences are remarkable for RAID systems (for details look >here<). - The stability of a system is at least as important as the performance. Especially users, who have installed the OS onto a single or RAIDed SSD, will realize stability issues, but not minimal performance differences, which are shown only by benchmark tests.
My favorite Intel AHCI/RAID drivers
for Intel systems from ICH7R/M up
(last updated: 09/09/2021)
Recommended for all Intel Chipset AHCI/RAID systems (except X79/X99/X299 Chipsets running in RSTe mode):
-
Intel RST drivers v11.2.0.1006 WHQL dated 05/30/2012
These latest "classical" Intel AHCI/RAID drivers do support all Windows Operating Systems from W2k/XP up to Win10 and are recommended for the following systems:- AHCI mode: Good choice for all Intel AHCI systems from ICH7 up to 5-Series Chipsets
- RAID mode: Probably best choice for all Intel RAID systems from ICH7R up to 7-Series Chipsets (look >here<)
Best matching Intel RAID ROM: v11.2.0.1527 (no Intel EFI RaidDriver available)
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- These are the latest "classical" Intel RST AHCI/RAID drivers, which are managing the Intel SATA AHCI/RAID Controller with just 1 single driver named iaStor.sys.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI RAID "SataDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
- Advantages:
a) They are running absolutely stable and will give the users AHCI/RAID system a very good performance (especially if being used with an SSD RAID0 configuration).
b) They are usable with all Windows Operating Systems from XP (32/64bit) up. - Disadvantages:
a) Not all features of the newest Intel chipsets are supported.
b) A matching EFI RAID BIOS module is not available (only valid for RAID users).
-
Intel RST(e) drivers v12.9.4.1000 WHQL dated 04/24/2014
Recommended for all Intel 5-Series, 6-Series and Mobile 7-Series Chipset systems, usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 (32/64bit) up.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v12.9.0.2006
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- These are the latest Intel AHCI/RAID drivers, which were optimized for 5-7 Series Chipsets.
- Contrary to the "classical" Intel RST drivers the RST(e) drivers have an additional SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI RAID "SataDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
-
Intel RST(e) drivers v13.1.0.1058 WHQL dated 05/28/2014
Recommended for Intel 7-Series Chipset Desktop systems and for X79/X99 Chipset systems, usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 (32/64bit) up.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v13.1.0.2126
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- These are the latest Intel AHCI/RAID drivers, which natively do fully support 7-Series. Additionally these drivers do support C600/C600+ Series Chipsets (only in AHCI mode unless having set the BIOS to "RST" mode).
- Like the later released v13.2.4.1000 ones these Intel RST(e) drivers v13.1.0.1058 are well developed and have a quite similar performance and stability.
- Contrary to the "classical" Intel RST drivers the RST(e) drivers have an additional SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI "RaidDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
-
Intel RST(e) drivers v13.2.8.1002 WHQL dated 07/09/2015
Recommended for Intel 8-, 9- and 100-Series Chipset systems, usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 (32/64bit) up.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v13.2.2.2224 (RAID OROM) resp. 13.2.0.2134 (EFI RaidDriver)
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- According to my experience these drivers are a very good choice for users with an Intel 8-, 9- and 100-Series Chipset system (for details look >here<).
- These Intel RST(e) drivers are well developed and will give the Intel 8-/9-Series Chipset systems a good performance and stability.
- Contrary to the "classical" Intel RST drivers the RST(e) drivers have an additional SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI "RaidDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
-
Intel RST(e) drivers v14.8.18.1066 WHQL dated 09/06/2017
Recommended for Intel X99 systems, usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 (32/64bit) up.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v14.8.2.2397
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- These currently latest Intel RST(e) drivers from the v14 platform are already well developed (contrary to the first v14 series drivers). They give modern Intel Chipset systems a good performance and stability.
- Contrary to the "classical" Intel RST drivers the RST(e) drivers have an additional SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI RAID "SataDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
-
For Intel RAID users: Intel RST(e) drivers v15.5.2.1054 WHQL dated 04/24/2017
According to my benchmark tests (look >here<) these drivers are the best choice for Intel 100-/200-Series Chipset systems running Win10 on a RAID0 array. They are usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 (32/64bit) up.
Warning for RAID5 array users: According to our Forum member rajkosto Intel RST RAID drivers from v15.5 series up are not recommended for RAID5 arrays. For details and alternative Intel RAID drivers for RAID5 arrays look >here<.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI "RaidDriver": v15.5.1.3017
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- These Intel RST(e) drivers from the v15.5 series are well developed (contrary to the first v15 platform drivers). They gave my 100-Series Intel Chipset system an extremely good RAID0 performance and stability.
- Contrary to the "classical" Intel RST drivers the RST(e) drivers have an additional SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI "RaidDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
-
Intel RST(e) drivers v15.9.8.1050 WHQL dated 07/31/2019
Recommended for Intel 100-/200-Series Chipset systems running in AHCI mode, usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 (32/64bit) up.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v15.9.3.3408
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- These are the latest RST(e) drivers and well developed (contrary to the first v15 platform drivers).
- Contrary to the "classical" Intel RST drivers the RST(e) drivers have an additional SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI "RaidDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
-
Intel RST drivers v17.11.3.10 WHQL dated 11/25/2022
Recommended for modern Intel Chipset systems from 300-/X299 Series up, only usable with Win10/11 x64.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: 17.8.4.4671
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:- These are currently the newest 64bit Intel RST drivers and optimized for being used with Win10/11 x64.
- These 64bit drivers do support all currently available modern SSD features (e.g. Optane).
- They do not contain an additional SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys and do not support older Windows Operating systems up to Win8.1.
- "TRIM in RAID0" is supported (Precondition: An actual Intel RAID ROM or EFI "RaidDriver" from v11 up is present within the BIOS).
Remark:
Regarding the usage of the modified drivers you should look into the start post of >this< thread.
Recommended for Intel 600/600+ Chipset series AHCI/RAID systems running in RSTe mode:
These are the latest Intel Rapid Storage Technology "Enterprise Edition" (RSTe) drivers, which belong to the v4 platform. Supported are all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 up. They are recommended for X79 Chipset systems running in "RSTe" mode.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v4.7.0.1017
These are the currently latest Intel Rapid Storage Technology "Enterprise Edition" (RSTe) drivers, which belong to the v5 platform. Supported are only 64bit Windows Operating Systems from Win8 up. They are recommended for X99 Chipset systems running in "RSTe" mode.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v5.5.5.1005
These are the currently latest Intel Rapid Storage Technology "Enterprise Edition" (RSTe) drivers, which belong to the v6 platform. Supported are only 64bit Windows Operating Systems from Win8 up. They are recommended for X299 Chipset systems running in "RSTe" mode.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v6.3.0.1005
These are the currently latest Intel Rapid Storage Technology "Enterprise Edition" (RSTe) drivers, which belong to the v7 platform. Supported are only 64bit Windows Operating Systems from Win8 up. They are recommended for the latest "Enterprise Edition" Chipset systems running in "RAID" mode.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM resp. EFI "RaidDriver" BIOS modules: v7.7.0.1054
Download links: Look >here<.
Comments:
- X99 users, who are running their Intel SATA ports in RST mode, should install the RST(e) drivers v14.8.18.1066.
- TRIM is supported in AHCI and RAID mode (incl. RAID0).
To make is easier for you to find the Intel RST/RSTe driver, which I recommend for your special AHCI or RAID system, here is a table:
Note: If you should find a better AHCI/RAID driver for your special Intel chipset, please let us know it!
| Intel Chipset/Southbr.: | Recommended Intel AHCI driver(s): | Recommended Intel RAID driver(s): |
| ICH7R/M, ICH8R/M and ICH9R/M | RST v11.2.0.1006 | RST v11.2.0.1006 |
| P45 and X58 Chipset/ICH10R | RST(e) v11.7.4.1001 | RST v11.2.0.1006 or RST(e) v11.7.4.1001 |
| 5-Series Chipsets (e.g. P55) | RST(e) v11.7.4.1001 or v12.9.4.1000 | RST v11.2.0.1006 or RST(e) v12.9.4.1000 |
| 6-Series Chipsets (e.g. P67+Z68) | RST v11.2.0.1006 or RST(e) v13.2.8.1002 | RST v11.2.0.1006 or v15.5.2.1054 (exc.RAID5) |
| 7-Series Desktop systems (e.g. Z77) | RST(e) v13.1.0.1058 or v13.2.8.1002 | RST v11.2.0.1006 or v15.5.2.1054 (exc.RAID5) |
| 7-Series Mobile systems (e.g. QM77) | RST(e) v12.9.4.1000 or v13.2.8.1002 | RST v11.2.0.1006 or RST(e) v13.1.0.1058 |
| 8-/9-Series Chipsets (e.g. Z87/Z97) | RST(e) v13.2.8.1002 | Intel RST v11.2.0.1006 (if poss.) or RST(e) v13.2.8.1002 |
| 100-/200-Series (e.g. Z170/Z270) | Intel RST(e) v13.2.8.1002 or v14.8.18.1066 | Intel RST(e) v15.5.2.1054 or RST v16.8.3.1003 |
| 300-Series Chipsets (e.g. Z370) | latest RST v16/17 platform drivers | latest RST v16/17 platform drivers |
| 400/500-Series Chipsets (e.g. Z470) | latest RST v18 platform drivers | latest RST v18 platform drivers |
| X79 Chipset | RST(e) v13.1.0.1058 WHQL | RST v11.2.0.1006 or RST(e) v13.1.0.1058 |
| X99 Chipset | RST(e) v14.8.18.1066 resp. RSTe v5.5.4.1036 | RST(e) v14.8.18.1066 resp. RSTe v5.5.4.1036 |
| X299 Chipset and up | latest RST v17 resp. RSTe v6/v7 platform drivers) | latest RST v17 resp. RSTe v6/v7 platform drivers |
Have fun!
Fernando
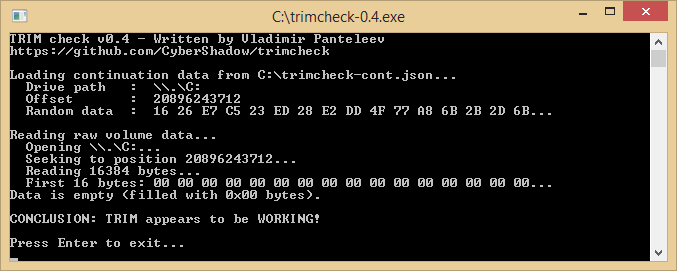
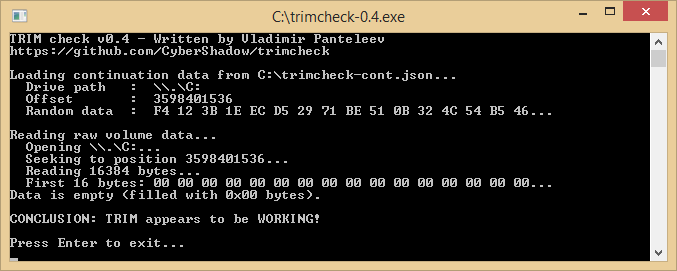
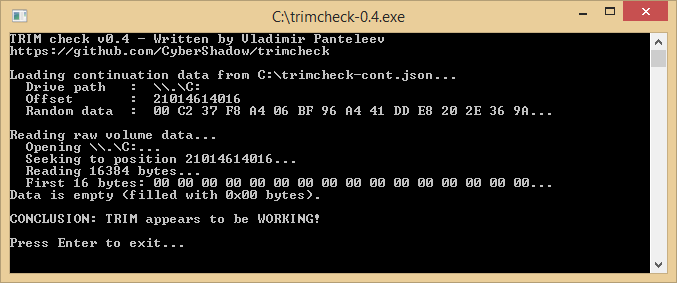
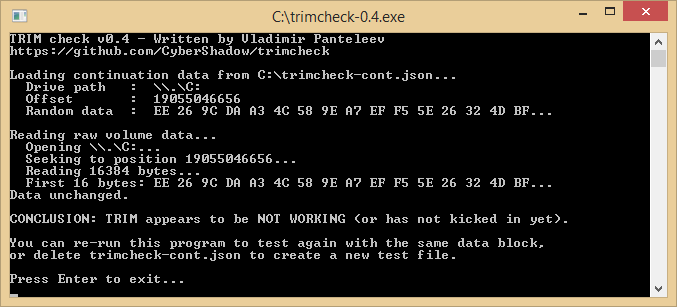
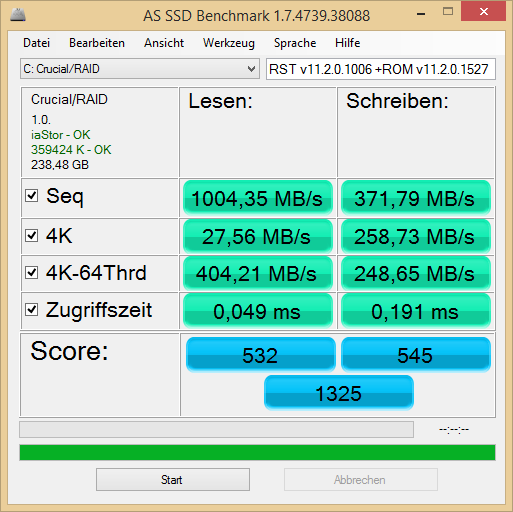
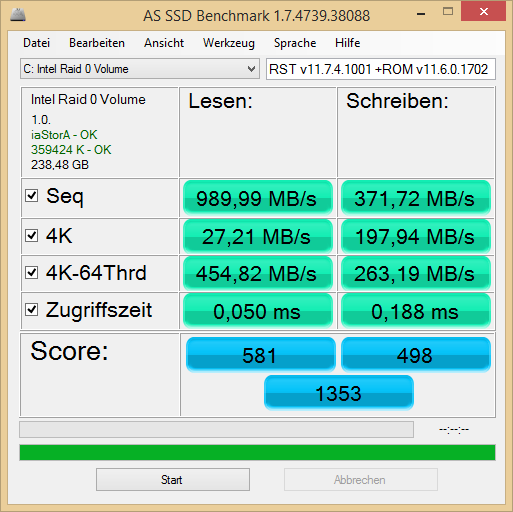
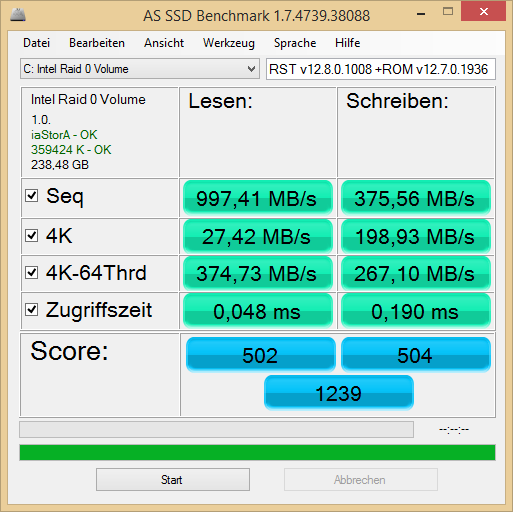
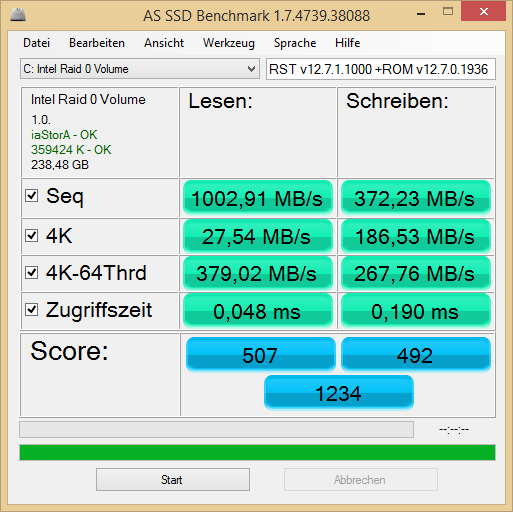


 . I forgot to mention that I am in dual boot (Win 8 pro x64, Win 7 Ultimate x64) both installed in UEFI.
. I forgot to mention that I am in dual boot (Win 8 pro x64, Win 7 Ultimate x64) both installed in UEFI. ,
,