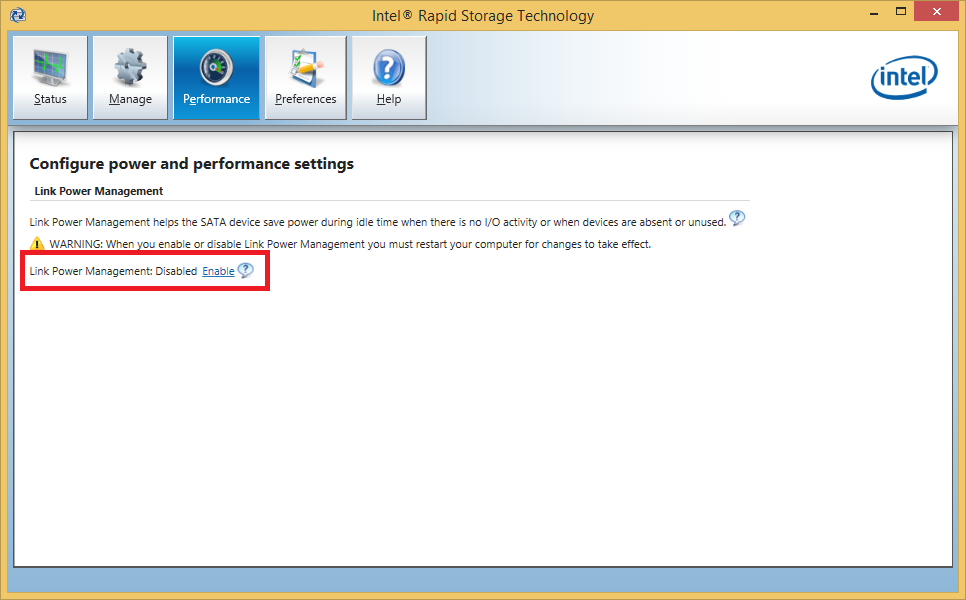
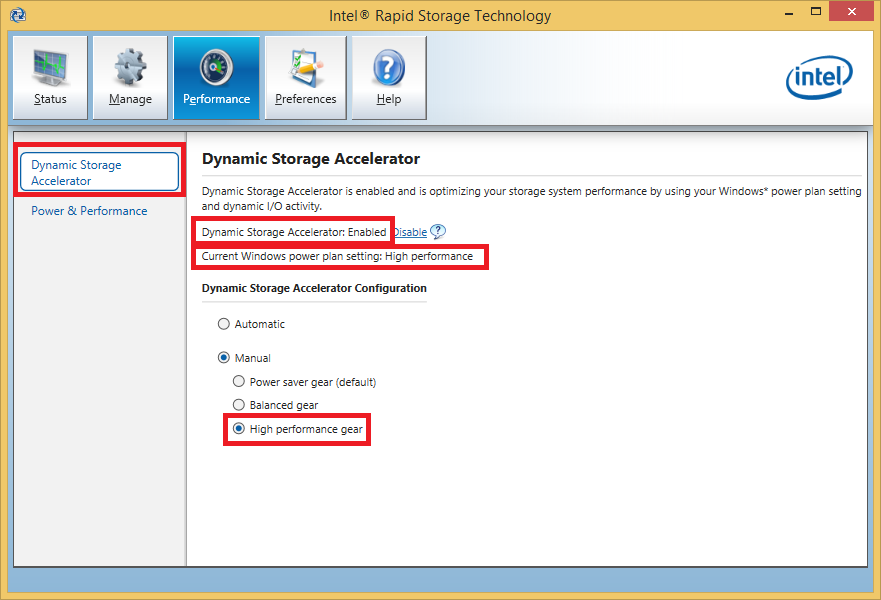
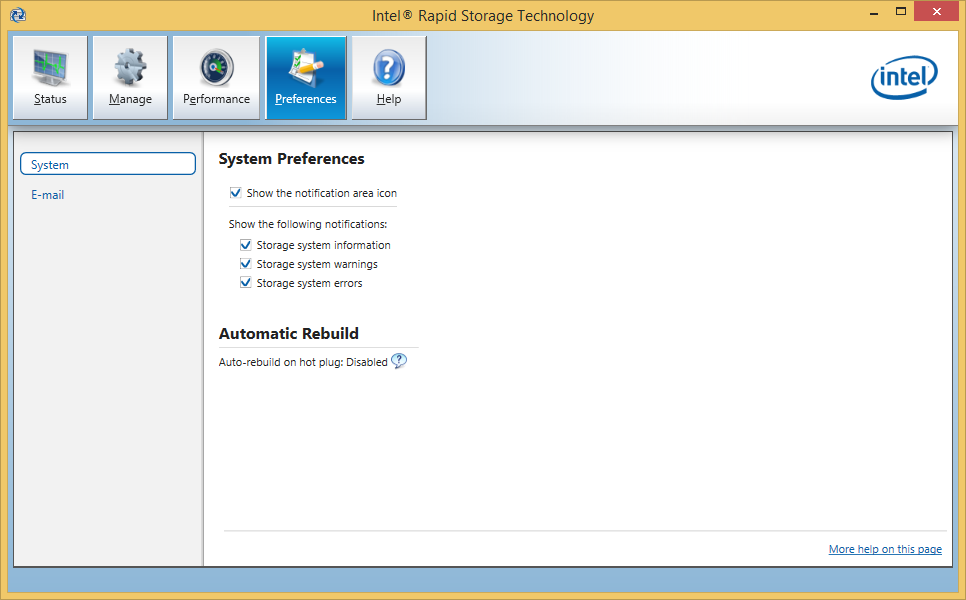
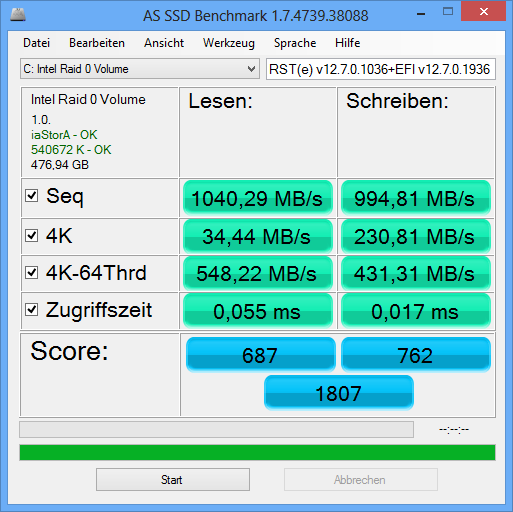
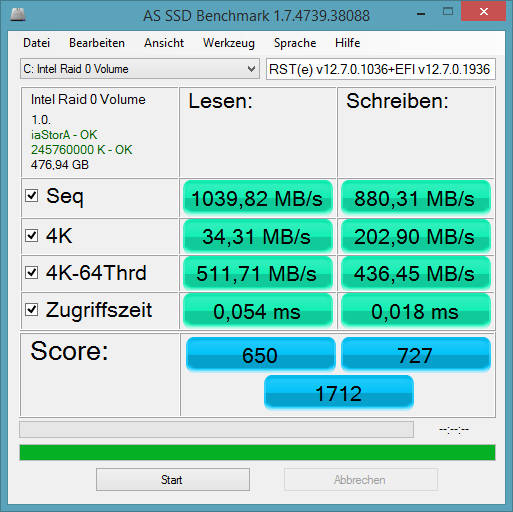
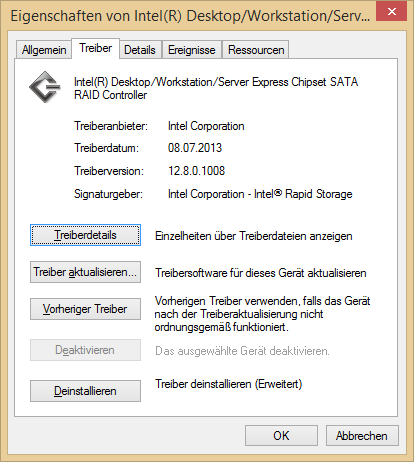
@ all users with an Intel AHCI or RAID system:
Intel’s RST/RSTe AHCI/RAID/VMD Drivers
inclusive details about
a) their RST Console Software (>post #2) and
b) the different Intel SATA AHCI/RAID Controllers (>post #3)
(last updated: 03/20/2025)
Changelog:
new: 64bit Intel VMD driver v19.5.8.1059 WHQL for Win10-11 x64 for Win10-11 x64 dated 10/28/2024
new: Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v19.5.8.1059.2 for Win10-11 x64 for Win10-11 x64 dated 12/05/2024
History of Intel’s Rapid Storage Technology
-
Details: (open/hide by a click)
Since the beginning of 2009 the Company Intel worked on the development of a completely new AHCI and RAID drivers and software technology named "Intel(R) Rapid Storage Technology" (IRST), which should replace the old Intel AHCI/RAID storage management named "Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager" (IMSM). The first final version of the IRST series was v9.5.0.1037\. It has been compiled by Intel on 10/23/2009, got the WHQL stamp from Microsoft on 10/09/2009 and has been officially released by Intel on 01/16/2010. In July 2011 Intel decided to change their IRST driver management and functionality by adding a separate SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys and renaming the AHCI/RAID driver from iaStor.sys to iaStorA.sys. The first IRST drivers series with the new 2-drivers-strategy were v11.5.0.1149 and released in March 2012\. Due to the presence of the additional SCSI filter driver the behaviour of these new IRST(e) drivers from v11.5 up is considerably different to the "conventional" RST series using just 1 single driver named iaStor.sys (last version: v11.2.0.1006) and very similar to the special IRST "Enterprise Edition" (IRSTe) v3.x.x.xxxx drivers for X79 chipsets. To make these differences as clear as possible for the users, I have added an "e" in brackets to all IRST drivers from v11.5 up.
Function and (dis)advantages of the IRST/IRST(e) Software
-
Details: (open/hide by a click)
The Software, which is part of all complete IRST packages and will be installed automaticly by running the installer, has the following main components:- the IRST Service (IAStorDataMgrSvc.exe), which is monitoring the IRST functions in the background as a special Win7/Win8 Service, and
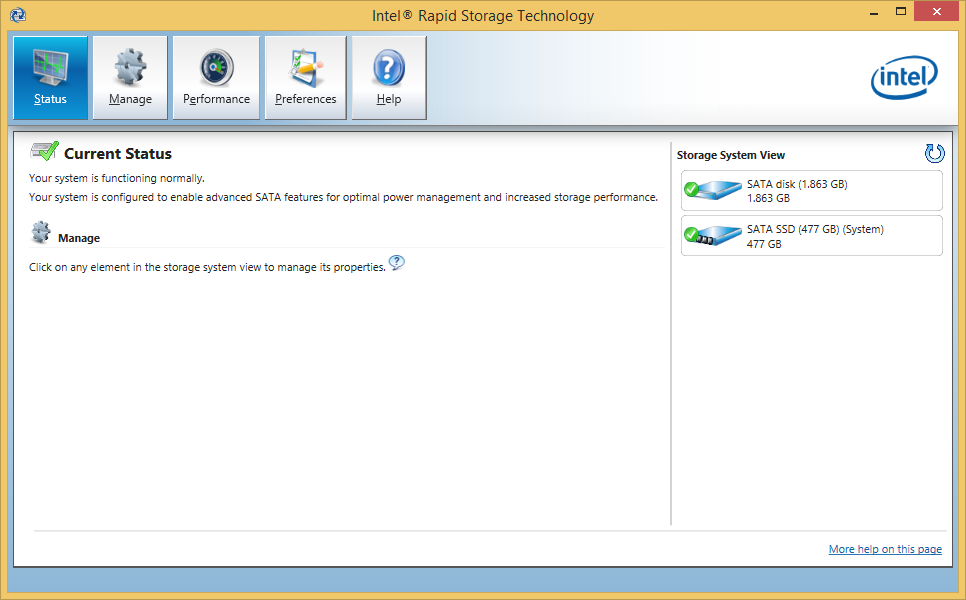
- the IRST Console (IAStorUI.exe), which gives the user some storage system informations and the opportunity to create a RAID array and to do some RAID settings from within the running OS.
Although the IRST Service and Console may be useful for Intel RAID or AHCI users, they are not really essential. The management of the Intel SATA AHCI and RAID Controllers is exclusively done by the IRST/IRST(e) drivers without the assistance of any IRST software component (except the “Write-back Caching” feature for RAID users). That is why it is possible to waive the IRST/IRST(e) Software completely and to just install the Intel AHCI/RAID drivers manually from within the Device Manager without risking any errors or malfunctions.
Advantages of the IRST Software installation:
- AHCI and RAID: monitoring of some details regarding the drives, which are connected to the Intel SATA AHCI resp.RAID Controller
- only RAID: creation, repairing and modification of a RAID array from within the OS
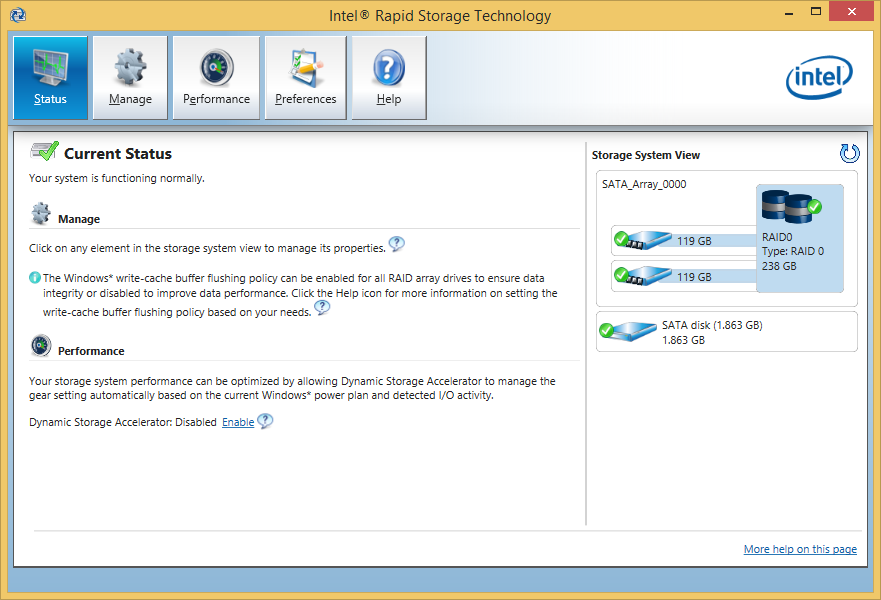
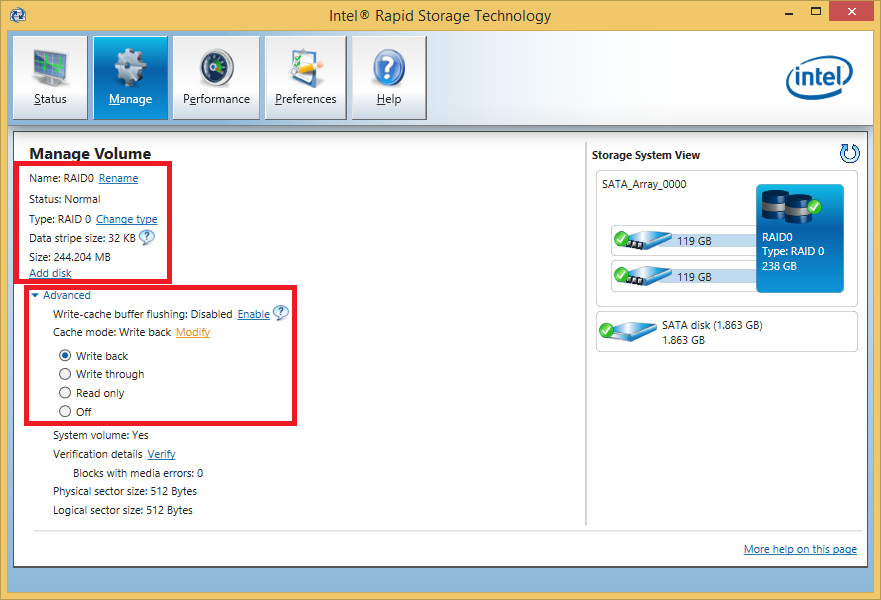
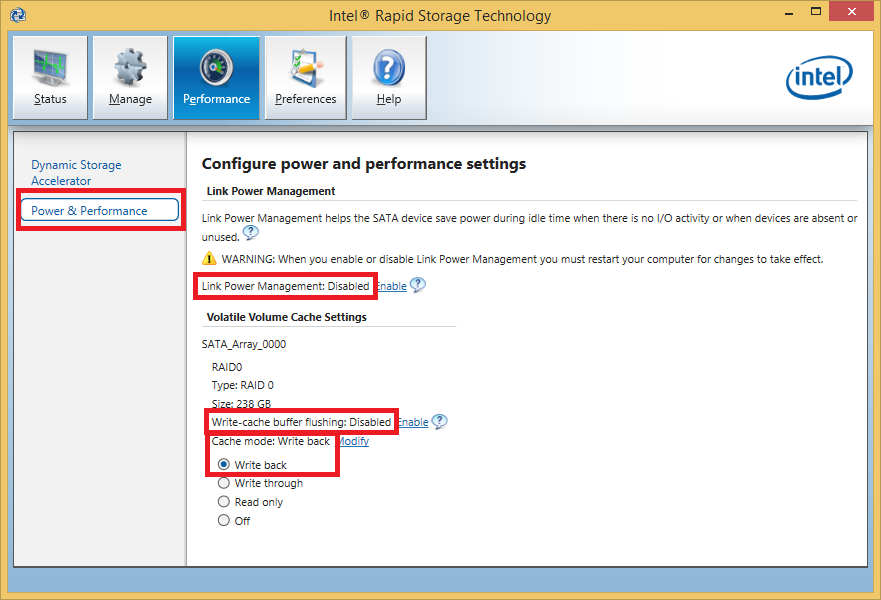
- only RAID: enabling of the “Write-Back-Caching” feature (boost of the write performance in RAID mode)
Disadvantages of the IRST Software installation:
- extension of the boot time
- additional demand of resources (the IRST Service usually runs permanantly in the background)
- possible increase of system instability (some IRST Software versions have severe bugs)
Tips:
-
AHCI users, who want a stable, performant system, should only load/install the IRST drivers and not the complete IRST package.
-
For RAID users I recommend to temporarily install the complete IRST/IRST(e) Drivers & Software Set just to get benefit of the “Write-Back-Caching” and the related write performance boost. After having enabled this feature, the “Intel(R) Rapid Storage Technology” software can be uninstalled from within the Control Panel.
Important: Once the “Write-Back-Caching” is enabled, the OS will keep this setting even after an update of the in-use RAID driver- no further RST Console Software installation will be required.
Download Links:
The *.RAR files have to be extracted by a tool, which supports the modern v5 RAR compression!
-
A. “Classical” Intel RST Drivers and their Software:
(These 32/64bit Intel RST driverpacks contain just 1 single driver named iaStor.sys and are designed for Intel systems with a Southbridge from ICH7R/M up except X79/X99/X299.)
-
Latest/best Intel RST drivers:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Intel RST drivers v10.1.0.1008:
- >32bit Intel RST AHCI/RAID Driver v10.1.0.1008 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST AHCI/RAID Driver v10.1.0.1008 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v10.1.0.1008 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Note: The Intel RST drivers v10.1.0.1008 WHQL are dated 11/06/2010.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM: v10.1.0.1008 -
Latest/best Intel RST drivers:
- >32bit Intel RST AHCI/RAID Driver v11.2.0.1006 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST AHCI/RAID Driver v11.2.0.1006 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v11.2.0.1006 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Note: The Intel RST drivers v11.2.0.1006 WHQL are dated 05/30/2012.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM: v11.2.0.1527
Mod+signed variants of some Intel AHCI/RAID drivers:
Download links to some “modified” versions of the previously mentioned Intel RST drivers and the related RST Software can be found within >this< thread. -
-
-
B. Intel RST(e) Drivers from v11.5 up and their Software:
(These Intel RST(e) driverpacks contain an AHCI/RAID driver named iaStorA.sys and additionally an SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys. They are designed for newer Intel chipsets except X79/X99 running in RSTe mode.)
-
Latest/best Intel RST(e) drivers from the v11 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v11.7.4.1001 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v11.7.4.1001 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v11.7.4.1001 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST(e) drivers v11.7.4.1001 WHQL are dated 03/05/2013.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM: v11.6.0.1702 -
Latest/best Intel RST(e) drivers from the v12 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v12.9.4.1000 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v12.9.4.1000 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v12.9.4.1000 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST(e) drivers v12.9.4.1000 WHQL are dated 04/07/2014.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v12.9.0.2006 -
Latest/best Intel RST(e) drivers from the v13 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Latest/best RST(e) v13.1 Series drivers: (credits go to station-drivers):
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v13.1.0.1058 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v13.1.0.1058 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v13.1.0.1058 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST(e) drivers v13.1.0.1058 WHQL are dated 05/02/2014. They are suitable for X79, X99, 7-Series Desktop systems and all 8-/9-Series Chipset systems running in AHCI mode.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v13.1.0.2126 -
Latest/best RST(e) v13.2 Series drivers: (credits go to Station-Drivers):
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v13.2.8.1002 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v13.2.8.1002 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v13.2.8.1002 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST(e) drivers v13.2.8.1002 WHQL are dated 07/09/2015.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v13.2.2.2224/v13.2.0.2134
-
-
Latest/best Intel RST(e) drivers from the v14 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Latest/best RST(e) v14.8 Series drivers:
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v14.8.18.1066 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v14.8.18.1066 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v14.8.18.1066 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST(e) drivers v14.8.18.1066 WHQL are dated 09/06/2017.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v14.8.2.2397
-
-
Latest/best Intel RST(e) drivers from the v15 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Latest/best RST(e) v15.2 Series drivers:
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v15.2.16.1060 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v15.2.16.1060 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v15.2.16.1060< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: These Intel RST(e) drivers v15.2.161060 WHQL are dated 03/30/2017 and usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 up. Only Intel 100-Series/C230 Chipsets, 200-Series Chipsets and other Chipsets with an Intel Skylake or KabyLake CPU are natively supported by these drivers. These Intel RST drivers are the last ones without Optane support and recommended for users with an Intel RAID1 or RAID5 array (for details please read >this< post written by rajkosto).
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v15.2.2.2775 -
Latest/best RST(e) v15.5 Series drivers:
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v15.5.2.1054 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v15.5.2.1054 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v15.5.2.1054 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: These Intel RST(e) drivers v15.5.2.1054 WHQL are dated 04/24/2017 and usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 up. Only Intel 100-Series/C230 Chipsets, 200-Series Chipsets and other Chipsets with an Intel Skylake or KabyLake CPU are natively supported by these drivers. These drivers additionally do support the “Intel(R) Optane™ Memory System Acceleration” and the “Intel(R) Smart Response Technology”.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v15.5.1.3017 -
Latest RST(e) v15.9 Series drivers:
- >32bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v15.9.8.1050 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >64bit Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers v15.9.8.1050 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST(e) AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v15.9.8.1051 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST(e) drivers v15.9.8.1050 WHQL are dated 07/31/2019 and usable with all Windows Operating Systems from Win7 up. Only Intel 100-Series/C230 Chipsets, 200-Series Chipsets and other Chipsets with an Intel Skylake or KabyLake CPU are natively supported by these drivers. These drivers additionally do support the “Intel(R) Optane™ Memory System Acceleration” and the “Intel(R) Smart Response Technology”.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v15.9.3.3408
-
-
Latest/best Intel RST drivers from the v16 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Latest RST v16.8 Series drivers:
- >64bit Intel RST AHCI/RAID/NVMe Drivers v16.8.5.1014 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
- >Intel RST AHCI/RAID/NVMe Drivers & Software Set v16.8.5.1014< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST drivers v16.8.5.1014 WHQL are dated 12/13/2022, the related Intel RST Drivers & Software Set is dated 01/19/2023.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v16.7.0.3513
-
-
Latest/best Intel RST drivers from the v17 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Latest RST v17.7 Series drivers:
-
>64bit Intel RST AHCI/RAID/NVMe Drivers v17.7.1.1010 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
-
>Intel RST AHCI/RAID/NVMe Drivers & Software Set v17.7.1.1010< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RST drivers v17.7.1.1010 WHQL are dated 03/02/2021.
Best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: 17.7.0.4404 -
-
Latest RST v17.11 Series drivers:
-
>64bit Intel RST AHCI-RAID-NVMe Drivers v17.11.3.1010 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
Theses drivers are dated 11/25/2022 and WHQL certified. Thanks to Dagal for the upload. -
>Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v17.11.3.1010.2< (>MIRROR<)
The Installer Set is dated 01/19/2023 and installs the Intel RST drivers v17.11.3.1010 WHQL. Thanks to westlake for the source file.
Currently best matching Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: 17.8.3.4687
-
-
-
Latest/best Intel RST drivers from the v18 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Pure drivers:
-
>64bit Intel RST AHCI+RAID+NVMe drivers v18.37.7.1013 WHQL< (>MIRROR<)
These drivers are dated 02/06/2023, WHQL certified and usable with Win10/11 x64 from v1703 up. Only the latest Intel SATA AHCI/RAID Controllers, but all Intel NVMe Controllers are supported by these drivers. Thanks to Dagal for having found and uploaded the driverpack. -
>64bit Intel RST VMD driver v18.8.0.1004 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This driver is dated 12/06/2023, WHQL certified and usable with Win10/11 x64 from v1703 up. Thanks to S-D for the source package.
-
-
Latest Complete Drivers & Software Set:
- >Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v18.7.7.1013.1 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This Set is dated 03/08/2023 and installs the Intel RST drivers v18.37.7.1013 WHQL resp. v18.7.7.1013 WHQL. Thanks to Station-Drivers for the source package.
Best matching Intel RAID EFI BIOS module: 18.31.3.5434
- >Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v18.7.7.1013.1 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
-
Latest/best Intel RST drivers from the v19 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Pure drivers:
- >64bit Intel RST VMD driver v19.5.8.1059 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This driver is dated 10/28/2024, WHQL certified and usable with Win10/11 x64 from v1703 up. Supported are the VMD Controllers with the DeviceIDs DEV_9A0B, DEV_09AB, DEV_467F and DEV_A77F. Thanks to S-D for the source package.
- >64bit Intel RST VMD driver v19.5.8.1059 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
Latest Complete Drivers & Software Set:
- >Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v19.5.8.1059.2 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This Set is dated 12/06/2024 and installs the Intel RST VMD and Hsa drivers v19.5.8.1059 WHQL dated 10/28/2024. Thanks to S-D for the source package.
Best matching Intel VmdDriver EFI BIOS module: v19.5.8.5786
- >Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v19.5.8.1059.2 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
-
Latest/best Intel RST drivers from the v20 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
Latest pure drivers:
- >64bit Intel RST VMD driver v20.2.4.1019 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This driver is dated 12/06/2024, WHQL certified and usable with Win10/11 x64. Supported are the VMD Controllers with the DeviceIDs DEV_9A0B, DEV_09AB, DEV_467F, DEV_A77F, DEV_7D0B and DEV_AD0B. Thanks to Station-Drivers for the driverpack.
- >64bit Intel RST VMD driver v20.2.4.1019 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
Latest Complete Drivers & Software Set:
- >Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v20.2.4.1019.4 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This Set is dated 02/05/2025 and installs the Intel RST VMD/Hsa drivers v20.2.4.1019 WHQL. Thanks to Station-Drivers for the source package.
Best matching Intel VmdDriver EFI BIOS module: v20.1.0.5817
- >Intel RST Drivers & Software Set v20.2.4.1019.4 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
Mod+signed variants of some Intel AHCI/RAID drivers:
Download links to some “modified” versions of the previously mentioned Intel RST(e) drivers and the related RST Software can be found within >this< thread.Important remarks regarding the usage of the 32/64bit RST(e) Drivers or the complete RST(e) Drivers and Software Set:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
- The Intel RST/RST(e) Software may require .NET Framework v3.0 or v3.5 for a proper installation and function.
Note: None of the Windows Operating Systems (not even Win8 and Win8.1) have the needed .NET Framework version working after a clean OS install!
To prevent any problems and error message after having installed the complete Intel RST/RST(e) package the first time, it is a good idea to make sure, that the needed .NET Framework version is already running, and to install the required .NET Framework version, if it’s not already done. Users, who forgot to install the needed .NET Framework version before they run the installer of the complete RST/RST(e) Set, will not be able to get access to the Intel RST Console, not even after having catched up the previously missed .NET installation.
Tip: This problem can be solved by just rerunning the installer of the RST(RST(e) Drivers & Software Set. - Because of the big structural and functional differences between the “classical” Intel RST driver (just using the iaStor.sys) and the newer Intel RST(e) drivers (using iaStorA.sys and additionally the SCSI driver iaStorF.sys), users should be very restrictive regarding the switch from one driver sort to the other. Extra dangerous is the “downgrade” from any RST(e) drivers (from v11.5 up) to any “classical” RST driver (latest: v11.2.0.1006). Before you are going to do that, a backup of the complete system partition is strongly recommended (in case that you are not able anymore to boot into the OS after the reboot).
- RAID resp. AHCI users, who had installed the RST software, should uninstall it, before they are going to install any other Intel AHCI or RAID driver or another complete RST/RST(e) package.
- Warning: According to the reports from our Forum members 100PIER and Frames the v17 and v18 platform Intel RST drivers may completely overtake the management of all existing Intel SATA/NVMe RAID arrays and additionally of all M.2/PCIe connected not RAIDed NVMe SSDs. To be able to recover the previously used different storage drivers, it is strictly recommended to set a “Restore Point” before starting the installation of these drivers.
- Users, who want to install any of the Intel RST(e) drivers (from v11.5 up) the first time, should unplug all removable devices, before they start with driver installation. Otherwise it is possible, that these devices will not be recognized anymore by the OS with the consequence, that the related drivers and software have to be reinstalled as well. This is not a bug of Intel’s RST(e) drivers or of the RST software, but a consequence of the completely new hardware detection procedure by the additional SCSI filter driver.
- Due to the severe changes of the complete storage device system by adding the SCSI filter driver, the first installation of the Intel RST(e) drivers while running Win7 comes up in 2 steps. That means, that the installation will be completed not until the user has done a second reboot.
- Only valid for Win7: After the successful installation of Intel’s RST(e) drivers you will recognize some changes within the Device Manager. They are caused by the installed Intel RST(e) SCSI filter driver.
Example: The Intel(R) SATA AHCI Controller may not be listed anymore as “IDE ATA/ATAPI Controller”, but now as “Storage Controllers”.
Note: The latest Windows Operating Systems from Win8 up neither need nor install the SCSI Filter driver named iaStorF.sys. - Warning: After having switched from any RST driver (iaStor.sys) to any of the RST(e) drivers (iaStorA.sys+iaStorF.sys) or vice versa you should never try to delete any of them from within the Windows\System32\Drivers folder (although they will not be in use anymore). If you do it nevertheless, you will get a BSOD during the next reboot. These drivers are needed by the OS.
-
-
C. Intel RSTe drivers and their Software:
(only for C600/C600+/C220 Series Chipsets like X79, X99 or X299)
These “Enterprise Edition” RST Drivers contain an additional SCSI Filter Driver like the RST(e) ones, but are just designed for Socket LGA 2011/2011-3 systems running in RSTe mode.
Only Intel RSTe RAID drivers from v3.8 up do fully support TRIM in RAID0, RAID1 and RAID10!-
Latest/best Intel RSTe drivers from the v3 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
>32bit Intel RSTe AHCI/RAID Drivers v3.8.1.1006 WHQL for Win7< (>MIRROR<)
-
>32bit Intel RSTe AHCI/RAID Drivers v3.8.1.1006 WHQL for Win8/8.1< (>MIRROR<)
-
>64bit Intel RSTe AHCI/RAID Drivers v3.8.1.1006 WHQL for Win7 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>64bit Intel RSTe AHCI/RAID Drivers v3.8.1.1006 WHQL for Win8/8.1 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>Complete Intel RSTe AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v3.8.1.1006 for Win7/8/8.1< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RSTe drivers v3.8.1.1006 WHQL are dated 09/25/2013.
Best matching Intel RSTe RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v3.8.0.1029 -
-
Latest/best Intel RSTe drivers from the v4 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
>32bit Intel RSTe SATA/sSATA AHCI/RAID Drivers v4.7.0.1098 WHQL for Win7 x86< (>MIRROR<)
-
>32bit Intel RSTe SATA/sSATA AHCI/RAID Drivers v4.7.0.1098 WHQL for Win8-10 x86< (>MIRROR<)
-
>64bit Intel RSTe SATA/sSATA AHCI/RAID Drivers v4.7.0.1098 WHQL for Win7 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>64bit Intel RSTe SATA/sSATA AHCI/RAID Drivers v4.7.0.1098 WHQL for Win8-10 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>Complete Intel RSTe AHCI/RAID Drivers & Software Set v4.7.0.1117 for Win7-10< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RSTe drivers v4.7.0.1098 WHQL are dated 11/24/2017.
Best matching Intel RSTe SATA RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v4.7.0.1017 -
-
Latest/best Intel RSTe drivers from the v5 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe SATA and sSATA AHCI/RAID Drivers v5.5.4.1036 WHQL for Win7 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe SATA and sSATA AHCI/RAID Drivers v5.5.4.1036 WHQL for Win8-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>compl. Intel RSTe Storage Drivers & Software Set v5.5.4.1036 for Win7-10< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Intel RSTe drivers v5.5.4.1036 WHQL are dated 04/09/2019.
Best matching Intel RSTe RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v5.5.5.1005 -
-
Latest/best Intel RSTe drivers from the v6 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe SATA/sSATA AHCI/RAID drivers v6.3.0.1022 WHQL for Win8-10 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe VROC NVMe RAID drivers v6.3.0.1022 WHQL for Win8-10 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>Intel RSTe Storage Drivers & Software Set v6.3.0.1031 for Win7-10 x64< (>MIRROR<)
Notes:
The Intel RSTe drivers v6.3.0.1022 WHQL are dated 01/13/2020, the Installer Set v6.3.0.1031 is dated 02/13/2020.
Best matching Intel RSTe RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v6.3.0.1005 -
-
Latest/best Intel RSTe drivers from the v7 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe SATA+sSATA VROC RAID drivers v7.8.3.1006 WHQL for Win8-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
These Intel RSTe drivers are dated 01/09/2023 and WHQL certified. -
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe VROC NVMe RAID drivers v7.8.3.1006 WHQL for Win8-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This Intel RSTe driver is dated 01/09/2023 and WHQL certified. -
>Intel VROC+NVMe+RAID Drivers & Software Set v7.8.0.1031 for Win8-10 x64< (>MIRROR<)
This Installer Set is dated 08/03/2022 and installs the Intel RSTe VROC SATA/sSATA/NVme drivers v7.8.0.1026 WHQL.
Best matching Intel RSTe RAID ROM/EFI BIOS module: v7.8.0.1012
-
-
Latest/best Intel RSTe drivers from the v8 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe VROC SATA RAID drivers v8.6.0.2003 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe VROC NVMe RAID driver v8.6.0.2003 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
Note: These drivers are dated 03/14/2024 and WHQL certified. Thanks to Station-Drivers for the source packs.
-
>Intel RSTe VROC RAID Drivers & Software Set v8.6.0.2003 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Installer Set is dated 04/17/2024 and installs the included Intel RSTe drivers v8.6.0.2003 WHQL dated 03/14/2024. Thanks to Station-Drivers for the source package.
Best matching Intel RSTe RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v8.0.0.4006
-
-
Latest Intel RSTe drivers from the v9 platform:
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe VROC SATA RAID drivers v9.0.5.1040 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
Note: This driver is dated 12/06/2024 and WHQL certified. Thanks to Station-Drivers for the source pack. -
>“pure” 64bit Intel RSTe VROC NVMe RAID driver v9.0.3.1028 WHQL for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
Note: This driver is dated 09/25/2024 and WHQL certified. Thanks to Dagal for the driverpack. -
>Intel RSTe VROC RAID Drivers & Software Set v9.0.5.1041 for Win10-11 x64< (>MIRROR<)
Notes: The Installer Set is dated 02/06/2025 and installs the included Intel RSTe VROC SATA RAID drivers v9.0.5.1040 dated 12/06/2024 and the Intel RSTe NVMe VROC driver v9.0.0.1836 WHQL dated 05/13/2024. Thanks to Station-Drivers for the source package.
Best matching Intel RSTe RAID ROM/EFI BIOS modules: v9.0.0.2018
-
-
Supported Operating Systems and Intel Southbridges:
- Operating Systems: Usually the listed Intel RST/RST(e)/RSTe drivers do support modern Windows Operating Systems from Win7 up. Windows XP is only supported by the Intel RST drivers (first section).
- Southbridges: As mentioned above, there are some restrictions regarding the supported Intel SATA AHCI/RAID Controllers. Nevertheless it is possible to get nearly all Intel AHCI/RAID drivers installed onto officially not supported Southbridges, if you are using any of my “modded” drivers (look >here<).
Integration of Intel RST/RST(e) drivers into a Win7/Win8 image:
All Intel RST/RST(e)/RSTe drivers can be integrated into the image of the OS (look >here<), but usually the Win7/Win8 Setup will detect automaticly the HDDs/SSDs running in AHCI or RAID mode. Only exception is the “clean” UEFI mode OS installation onto a RAID array by using an actual EFI RAID SataDriver module. In this case you should either integrate a suitable up-to-date 32/64bit Intel RAID driver into the OS image or prepare a separate USB flash drive with such driver.
Information for SSD users regarding TRIM support:
- All 32/64 Intel AHCI Drivers since v9.6.1014 do fully support TRIM. That means, that the related cells of the SSD/SDDs will be cleaned and reusable directly after having deleted their content of data.
- According to Intel all recently released Intel RAID Drivers do support TRIM as well for SSDs, which are running in RAID mode (only exception: SSDs, which are members of a RAID array).
- For Intel 7-Series Chipsets the actual Intel RAID drivers from v11 up (except v12.5.0.1066) natively do support TRIM even within an Intel RAID0 array (only in combination with an Intel RAID ROM v11 or v12). Users with an Intel P55/P67/Z69/X79 Chipset are able to get the “TRIM in RAID0” feature as well, if they are using a BIOS with an especially modified Intel RAID ROM or EFI RAID “SataDriver” module. For details please look into >this< thread.
a) Correlation between Intel RAID driver and BIOS Module
-
Details: (open/hide by a click)
-
This chapter is only relevant for RAID users. As long as the Intel SATA Controller is running in AHCI mode, the presence and the version of the related Intel RAID BIOS modules don’t matter, because they will not be used by the AHCI system.
Generally the functionality and the performance of all SATA RAID Controllers depends on
- a) the specific in-use RAID driver(s) and
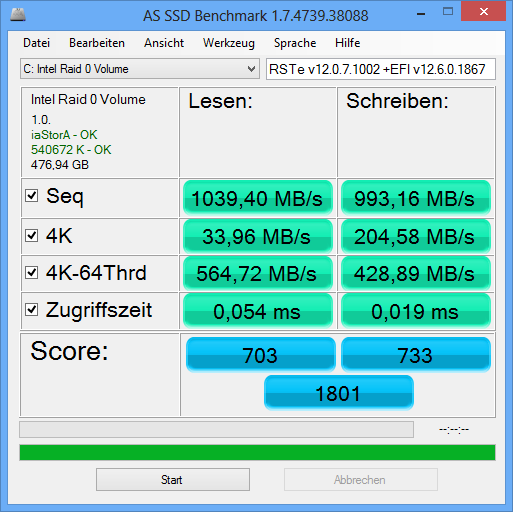
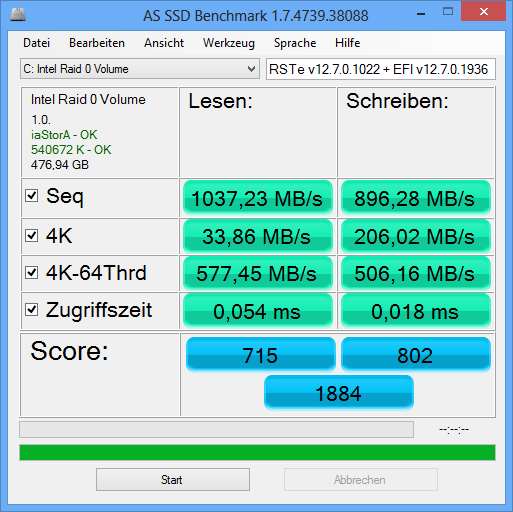
- b) the related Intel RAID Controller “Firmware” modules (as part of the mainboard BIOS) (here: Intel’s RAID OROM resp. EFI “SataDriver”/“RaidDriver” modules).RAID users will get the best results, if the RAID driver version and the RAID Controller “Firmware” match each other, that means belong to the same development branch (example: RST v11.2.x.xxxx or RST(e) v12.6.x.xxxx).
Due to the relationship between the in-use Intel RAID driver and the related Intel RAID ROM/EFI BIOS module versions the Intel RAID functions and features are limited by the oldest component of them. Users may even not be able to get the newest Intel RAID drivers installed as long as the BIOS contains an absolutely outdated Intel RAID ROM module version.
As a consequence of the mentioned dependency between the Intel RAID driver and OROM module version it is a good idea to check the “Firmware” (OROM) version of the Intel SATA RAID Controller and to compare it with the version of the actually available RAID ROM modules. RAID users will see the currently working RAID ROM version of their system very quick as popup while booting (unless they have disabled the OROM popup within the BIOS). Alternatively they can enter the “Intel RAID Configuration Utility” by hitting CTRL+I at startup, which will show the Intel RAID ROM version very clearly. Users, who are currently running their system drive in “AHCI” mode, should change temporarily the SATA Cotroller mode to “RAID”, if they want to see the Intel RAID ROM (don’t forget to undo the BIOS setting after the test).
RAID users, who verify, that the Intel RAID ROM/EFI “RaidDriver” version is outdated and doesn’t match the actually running or desired Intel AHCI/RAID driver version, should look into the support pages of their mainboard/system manufacturer and search for a newer BIOS with an updated Intel RAID ROM/“RaidDriver” module. If they don’t find it, but want it nevertheless, they may update the related BIOS module of their mainboard BIOS themself (only recommended for experienced users, who know about the risks and do the needed precaution actions). They will find a detailed guide about how to do it within >this< Forum section.
-
b) Switch from Intel RST to RST(e) drivers (or vice versa)
-
Details: (open/hide by a click)
- Generally all users with an Intel AHCI or RAID system and a Southbridge from ICH7R/M up are free to decide, if they want to use either
-
a) one of the “classical” Intel RST drivers (latest: v11.2, using just 1 single driver named iaStor.sys)
-
b) any of the newest Intel RST(e) drivers (from v11.5 up, using the AHCI/RAID driver named iaStorA.sys and additionally an SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys).According to my experiences actual Intel AHCI and RAID Controllers are working fine with both types of the Intel AHCI/RAID drivers. Nevertheless there are some noticeable differences, which depend on the specific hardware configuration and the preferences of the users (for details you may look into >this< thread). That is why I recommend to test it out yourself, which Intel AHCI/RAID drivers series (RST or RST(e)) and which driver version is the best for you and your system.
Usually the “update” or “downgrade” of the in-use Intel AHCI/RAID driver version will not induce any problems, but the users should be aware of the fundamental differences between the RST and the RST(e) drivers. That is why I strictly recommend to uninstall the previously used RST software from within the “Control Panel” and to reboot after having done that, before any other Intel RST or RST(e) package should be installed.
Attention: If possible, you should avoid a “downgrade” from any of the Intel RST(e) drivers to one of the “classical” Intel RST versions. This procedure may even end up with endless BSODs while rebooting and the necessity to do a fresh install of the OS.
Additionally there seems to be a bug regarding the uninstall procedure of some Intel RST(e) driver versions, with the result, that the SCSI filter driver named iaStorF.sys may be still active in the background and lowers the performance of the system permanently. This issue is caused by some RST(e) registry entries, which obviously are not deleted by the uninstall commands. Further informations regarding this issue and a guide how to solve this problem can be found >here<.
Tips:
- The previously running “Intel(R) Rapid Storage” software should be uninstalled before you are going to install any other Intel AHCI/RAID driver package.
- If you want to compare different Intel RST and RST(e) drivers, it will be a good idea to start the tests with an RST driver, because the later “upgrade” to any of the RST(e) drivers will be safe (contrary to the vice versa direction).
-
- Generally all users with an Intel AHCI or RAID system and a Southbridge from ICH7R/M up are free to decide, if they want to use either
Note: Due to the limited place and for a better overview I have moved the informations about the Intel RST Console Software and the related screenshots into the second post of this thread.
Good luck with Intel’s RST resp. RST(e) drivers!
Fernando